
Guard Column vs In-Line Filter: Which One Should You Use?
In HPLC, most performance problems don’t start at the detector — they start before the column. High back
Home » Sugar Reference Standards
At uHPLCs, we specialize in the preparation of high-quality reference standards designed to meet the strict requirements of research, analysis, and calibration. Our solutions ensure accuracy, traceability, and consistency across pharmaceutical, food, chemical, and industrial applications.
We provide a wide selection of reference standards, including:
In addition, we also offer custom preparation services to meet unique project needs, ensuring every reference standard delivers dependable performance.
Get Expert Guidance and Customized Solutions for Accurate Reference Standards

uHPLCs provides a comprehensive portfolio of reference standards, covering:
This wide coverage reduces the need to source from multiple suppliers, ensuring consistency, reliability, and efficiency for laboratories and research facilities.


This flexibility makes uHPLCs an ideal partner for academic labs, pharmaceutical companies, and industrial QC teams.
At uHPLCs, we understand that every laboratory, research project, and industrial application may require unique reference standards beyond standard catalogs. That’s why we provide a tailored Custom Reference Standards Service designed to meet your specific analytical and regulatory needs.

 What We Offer
What We Offer Why Choose uHPLCs Custom Service?
Why Choose uHPLCs Custom Service?




As Follow is Some Frequently Questions People Asked
A reference standard is a highly pure, well-characterized substance used as a benchmark in scientific analysis, quality control, and regulatory testing. It acts as a calibration point or comparison material to verify the identity, concentration, and performance of test samples.
In pharmaceutical, food, chemical, and research laboratories, reference standards are essential to ensure accuracy, reproducibility, and compliance. For example, when testing a drug’s purity using HPLC, a certified reference standard of that compound is injected to compare retention time, peak shape, and response factor.
At uHPLCs, we supply reference standards covering carbohydrates, vitamins, amino acids, fatty acids, and pharmaceutical impurities, providing global researchers with reliable materials for consistent results.
In scientific research, a reference standard serves as a control material against which experimental results are compared. For example:
In drug discovery, it helps validate the identity and purity of a synthesized compound.
In food analysis, sugar and vitamin standards ensure accurate quantification of nutrients.
In clinical research, amino acid or metabolite standards support biomarker studies.
By using validated reference standards, researchers minimize variability and ensure their data is credible, reproducible, and publishable in peer-reviewed journals.
uHPLCs supports research institutes and universities worldwide by offering flexible packaging (mg to g) and custom preparation of rare compounds.
A basic reference standard usually refers to the most fundamental or primary standard of a compound, established and recognized by international or national authorities (e.g., USP, EP, JP). These are often termed pharmacopoeial reference standards and are used for:
Method validation
Instrument calibration
Identity/purity confirmation
In routine laboratories, however, the term may also refer to any high-purity compound used as a reference for analysis.
uHPLCs provides both basic common standards (e.g., glucose, vitamin C, glycine) and specialized rare standards, enabling labs to cover both everyday and advanced testing needs.
In the United States, reference standards are primarily provided by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP). USP Reference Standards are official substances used to ensure drugs and healthcare products meet quality specifications. They are widely recognized by the FDA and regulatory bodies worldwide.
However, USP standards can be very expensive and sometimes limited in coverage. For routine lab use, many researchers choose alternative suppliers like uHPLCs, who provide high-purity, traceable, cost-effective equivalents for vitamins, amino acids, fatty acids, and impurities. These are ideal for method development, education, and non-regulatory QC, while still aligning with scientific best practices.
Producing a reference standard involves several key steps:
Synthesis or isolation of the target compound.
Purification to very high purity (typically ≥98–99%).
Characterization using multiple techniques (HPLC, NMR, MS, IR, elemental analysis).
Documentation – providing a Certificate of Analysis (COA) with CAS number, molecular structure, purity data, and traceability.
Stability testing to ensure the standard remains reliable over time.
At uHPLCs, we follow strict processes to prepare both catalog standards and custom standards. Clients can request OEM or tailor-made synthesis, with full confidentiality guaranteed.
Yes—using reference standards is mandatory in regulated industries such as pharmaceuticals, food safety, and environmental testing. Without them, there is no way to confirm that your analytical results are valid.
Pharmaceuticals: Required for FDA/EMA submissions.
Food Industry: Needed to quantify vitamins, sugars, and additives.
Research: Essential for reproducibility and credibility.
Without reference standards, test results may be inaccurate, non-compliant, and rejected by regulators. This is why labs worldwide rely on suppliers like uHPLCs for consistent, high-purity standards.
When writing a lab report or regulatory submission, reference standards must be documented clearly. A proper entry should include:
Name of compound (e.g., Vitamin B1 – Thiamine Chloride)
CAS number
Molecular formula
Supplier and lot number (e.g., uHPLCs, Lot #xxxx)
Purity and specification data
Example report entry:
“Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid), Reference Standard, uHPLCs, CAS 50-81-7, Purity ≥ 99%, Lot 2025-01, used for calibration of HPLC analysis of food supplements.”
Failure to use or cite reference standards correctly can have serious consequences:
Regulatory rejection of pharmaceutical submissions.
Invalid data in food safety testing.
Scientific credibility loss if results cannot be reproduced.
Financial losses due to repeat testing or product recalls.
For research publications, incorrect referencing may lead to manuscript rejection. In regulated industries, it may even trigger legal or compliance penalties.
Using properly documented and traceable standards from uHPLCs ensures that your testing process is reliable, compliant, and recognized by global partners.
Contact uHPLCs Today for Any Questions for HPLC / UHPLC

In HPLC, most performance problems don’t start at the detector — they start before the column. High back
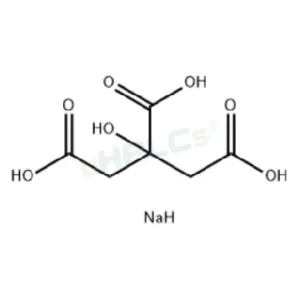
Uridine 5’-triphosphate Trisodium Salt (UTP-Na₃) Reference Standard | CAS 19817-92-6 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: U-D25015X Chemical

Glutathione (G-SH) Reference Standard | CAS 70-18-8 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: G-D25016X Chemical Name: Glutathione (G-SH)

Adenosine 5’-triphosphate Disodium Salt Reference Standard | CAS 987-65-5 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: A-D25014X Chemical Name:

Butafosfan Reference Standard | CAS 17316-67-5 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: B-D25013X Chemical Name: Butafosfan Category: Drug

Calcium Gluconate Reference Standard | CAS 299-28-5 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: C-D25012X Chemical Name: Calcium Gluconate

Magnesium L-aspartate Reference Standard | CAS 2068-80-6 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: M-D25011X Chemical Name: Magnesium L-aspartate
WhatsApp us
Subscribe for exclusive offers and updates on new arrivals