
Why HPLC Frits Clog ?
1. Introduction: What Is an HPLC Frit and Why It Matters As you know, In
Home » HPLC Analytic for Horticultural Research
Contact uHPLCs Today for Any Questions for HPLC / UHPLC

1. Introduction: What Is an HPLC Frit and Why It Matters As you know, In

High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) delivers reliable separation and quantification across pharmaceuticals, biological samples, natural products,

Introduction Ever struggled to decide which HPLC column to use for your analysis? You’re not
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is an invaluable tool in horticultural research, playing a crucial role in various applications:

High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful tool extensively used in horticultural research, due to its capacity to precisely separate, identify, and quantify compounds present in complex mixtures. Here are some of its key applications:
Analysis of Phytochemicals: HPLC allows the detection and quantification of phytochemicals, including phenolics, flavonoids, and carotenoids, present in fruits, vegetables, and other plant tissues. This contributes to our understanding of the nutritional and medicinal properties of horticultural crops.
Assessment of Plant Health: HPLC is used to monitor plant health by analyzing the presence and concentration of stress markers, hormones, or nutrients in plant tissues. This assists in early detection of plant diseases or nutrient deficiencies.
Detection of Pesticide Residues: HPLC aids in the identification and quantification of pesticide residues on fruits and vegetables, ensuring consumer safety and regulatory compliance.
Breeding Programs: By analyzing the genetic and chemical profiles of plant varieties, HPLC aids in plant breeding programs aimed at improving crop yield, disease resistance, and nutritional quality.
Soil Analysis: HPLC is used to analyze soil samples for the presence of various nutrients and contaminants, aiding in the optimization of soil health for horticultural applications.
Quality Control: HPLC is a reliable method for assessing the quality of horticultural products, including the determination of sugars, acids, and other compounds that contribute to the taste and nutritional value of fruits and vegetables.
Environmental Impact Assessment: By analyzing leachates and run-off from horticultural farms, HPLC assists in understanding and mitigating the environmental impact of horticultural practices.
In each of these applications, HPLC provides precise and reliable data, making it an essential analytical tool in horticultural research.
Advantages of Using HPLC in Horticultural Research

By addressing these and other questions, HPLC proves to be an indispensable tool in horticultural research, aiding in everything from product quality assessment to environmental conservation.
HPLC can be used to identify and quantify various compounds that contribute to the quality of horticultural products. These can include sugars, organic acids, vitamins, and phytochemicals such as polyphenols and carotenoids. By assessing the concentration of these compounds, researchers can determine the nutritional content, flavor profile, and overall quality of the product. This information is essential for breeders who aim to improve these qualities, and for growers to assess the effects of different cultivation practices.
Yes, HPLC is an extremely effective tool for detecting and quantifying pesticide residues in horticultural products. The technique can separate and identify a wide variety of pesticides, even at very low concentrations. This is crucial for ensuring the safety of fruits and vegetables for consumption and for compliance with regulatory standards. The results can guide farmers in adopting more sustainable pest management strategies.
HPLC can aid in plant breeding by providing detailed information about the chemical and genetic profiles of different plant varieties. By analyzing metabolites and phytochemicals, researchers can identify varieties with desirable traits, such as higher nutritional content, better flavor profiles, or increased resistance to pests and diseases. This information can guide selective breeding efforts to develop improved plant varieties.
Absolutely. HPLC can be used to analyze plant tissues for various markers of plant health. This could include hormones, stress markers, or nutrients. Changes in the concentrations of these substances can provide early warning signs of plant disease, nutrient deficiency, or other stress conditions. By allowing early detection and intervention, HPLC can help optimize plant health and crop yields.
HPLC can be used to analyze soil and water samples for the presence of contaminants such as pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals used in horticulture. By assessing the concentration and distribution of these substances, researchers can understand the environmental impact of horticultural practices. This information can guide efforts to develop more sustainable farming practices and mitigate environmental harm.
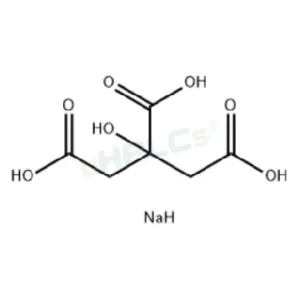
Uridine 5’-triphosphate Trisodium Salt (UTP-Na₃) Reference Standard | CAS 19817-92-6 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: U-D25015X Chemical Name: Uridine 5’-triphosphate Trisodium Salt (UTP-Na₃) Category:

Glutathione (G-SH) Reference Standard | CAS 70-18-8 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: G-D25016X Chemical Name: Glutathione (G-SH) Category: Drug Impurity Standard CAS Number: 70-18-8

Adenosine 5’-triphosphate Disodium Salt Reference Standard | CAS 987-65-5 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: A-D25014X Chemical Name: Adenosine 5’-triphosphate Disodium Salt Category: Drug Impurity
WhatsApp us
Subscribe for exclusive offers and updates on new arrivals