
A Complete Guide to Guard Columns, Benefits, Applications, and Best Practices
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) delivers reliable separation and quantification across pharmaceuticals, biological samples, natural products,
Contact uHPLCs Today for Any Questions for HPLC / UHPLC

High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) delivers reliable separation and quantification across pharmaceuticals, biological samples, natural products,

Introduction Ever struggled to decide which HPLC column to use for your analysis? You’re not

Introduction Ever wondered how scientists ensure your medicine is pure, or your drinking water is
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a cornerstone in academic research and analytics, enabling precise and reliable analysis of various substances. Utilized across diverse fields, from biochemistry to environmental science, it allows researchers to separate, identify, and quantify compounds in complex mixtures.
HPLC facilitates the study of drug interactions, the tracking of environmental pollutants, and the investigation of biochemical processes, contributing significantly to academic advancements and breakthroughs.

High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) has a broad range of applications in academic analytics across various fields. Here are some of them:
Biochemistry: HPLC is extensively used in biochemistry for studying biological samples. It aids in the analysis and quantification of proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, and various metabolites.
Pharmaceutical Sciences: In academic research, HPLC is widely used in drug discovery and development. It helps in the analysis of new drug candidates, studying drug-drug and drug-biomolecule interactions, and monitoring drug stability.
Environmental Sciences: HPLC is used in the identification and quantification of environmental pollutants. It aids in studying the distribution and fate of various contaminants in the environment.
Food and Nutrition Sciences: HPLC assists in analyzing the nutritional content of food and beverages, such as vitamins, sugars, and fatty acids. It’s also used to detect food contaminants and adulterants.
Forensic Sciences: HPLC is used in forensics for the analysis of various types of evidence, such as drug identification in biological samples or the analysis of trace evidence at crime scenes.
Chemistry: HPLC is a vital tool in academic chemistry labs, used in studying reaction kinetics, purifying chemical compounds, and synthesizing new materials.
In each of these fields, HPLC provides researchers with precise, reliable, and reproducible data, making it a vital tool in academic analytics.
When performing HPLC analytics in an academic setting, there are several factors to consider to ensure accurate, reliable, and reproducible results:
Sample Preparation: The quality and consistency of your results will largely depend on how well your sample is prepared. This includes proper sampling techniques, effective homogenization, correct sample dissolution, and appropriate storage conditions.
Choice of HPLC Method: Selecting the appropriate HPLC method for your analysis is crucial. This involves choosing the right type of HPLC (normal phase, reverse phase, ion exchange, size exclusion, etc.), the correct column, and the optimal mobile phase composition.
System Calibration: Regular calibration of your HPLC system is essential to ensure it operates accurately and provides reliable results. This includes calibration of the pump pressure, temperature controls, detector response, and gradient composition.
System Maintenance and Use of High-Quality Components: Regular maintenance of the HPLC system, including the use of high-quality components such as UPLC In-line Filters, will ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the system. This includes routine cleaning, timely replacement of worn-out parts, and preventive measures against contamination.
Data Analysis: Proper interpretation of HPLC data is critical. Understanding the factors that influence peak shape, retention time, and resolution will help in accurate identification and quantification of your analytes.
Safety: Working with HPLC systems involves handling potentially hazardous chemicals. Adherence to safety guidelines, proper waste disposal, and use of personal protective equipment are crucial.
Documentation: Keeping detailed records of each step in your process, including any troubleshooting or changes made, will improve the reproducibility of your results and assist in troubleshooting if issues arise.
By giving attention to these aspects, you can ensure that your HPLC analytics provide the valuable and reliable data you need for your academic research.

Duis condimentum nunc metus, maximus porta velit temporin. Intincidunt leo viverra, sodales ex eu, posuere purus. Duis in augue vestibulum, aliquet nulla vitae, tempus tellus.
Choosing the best HPLC method requires a thorough understanding of your sample and the objectives of your analysis. Consider the nature of your analytes, their solubility, their chemical properties, and their potential interactions with the stationary and mobile phases. Consult relevant literature or databases for similar research studies to get an idea of what methods have been effective in comparable scenarios. Additionally, take advantage of column and solvent manufacturers’ resources, as they often provide guides and tools to help choose the appropriate method.
Broad or tailing peaks in HPLC can be caused by several factors. These include interactions between your analyte and the stationary phase, improperly prepared or loaded samples, sub-optimal column conditions, or issues with the mobile phase. To troubleshoot this, you may need to adjust the pH of your mobile phase, change your column, optimize your sample preparation procedure, or investigate your instrument for potential hardware issues.
Improving HPLC sensitivity can be achieved in a few ways. First, consider optimizing your method — this could involve changing the type or concentration of your mobile phase, adjusting the column temperature, or altering the flow rate. Additionally, ensure that your HPLC system, including detectors, is properly calibrated and maintained. Utilizing a more selective detector or a column with smaller particle size can also enhance sensitivity.
Lack of reproducibility in HPLC analysis can stem from many sources. Sample preparation variability, inconsistent operating conditions, or lack of system maintenance could be to blame. Always make sure to prepare samples consistently, run standards regularly, and ensure that your HPLC system,
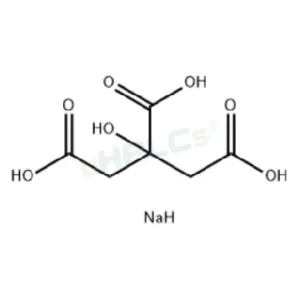
Uridine 5’-triphosphate Trisodium Salt (UTP-Na₃) Reference Standard | CAS 19817-92-6 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: U-D25015X Chemical Name: Uridine 5’-triphosphate Trisodium Salt (UTP-Na₃) Category:

Glutathione (G-SH) Reference Standard | CAS 70-18-8 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: G-D25016X Chemical Name: Glutathione (G-SH) Category: Drug Impurity Standard CAS Number: 70-18-8

Adenosine 5’-triphosphate Disodium Salt Reference Standard | CAS 987-65-5 | High-Purity Reference Materiel Product Code: A-D25014X Chemical Name: Adenosine 5’-triphosphate Disodium Salt Category: Drug Impurity
WhatsApp us
Subscribe for exclusive offers and updates on new arrivals